Spatial computing is an emerging paradigm that blends the digital and physical worlds through AR (augmented reality), VR (virtual reality) and AI. In this vision, computers “naturally integrate” into our environment, overlaying digital content onto real scenes weforum.org. Modern headsets – from Microsoft’s HoloLens to Apple’s Vision Pro – illustrate this fusion: users can see real surroundings with 3D holograms superimposed, and interact with them as if they were tangible weforum.org. Meanwhile, AI itself is evolving from a passive tool into an autonomous, goal-driven agent. Today’s AI systems can perceive their surroundings, learn, plan and act on complex tasks with minimal human input wwt.comaws.amazon.com. For example, AWS notes that the latest AI agents can reason, plan trips or even pay bills on our behalf aws.amazon.com. Together, spatial computing and advanced AI promise a future of truly immersive technology – intelligent agents and digital objects coexisting in our physical world.

Figure 1: Spatial Computing and how is it advancing life & work? (https://www.plugxr.com/augmented-reality/what-is-spatial-computing/)
What is Spatial Computing?
Spatial computing refers to technologies that understand and augment our 3D physical space. It encompasses AR, VR, mixed reality (MR), and related XR interfaces weforum.org. In practice, this means devices (often head-mounted) use sensors like cameras, depth cameras and LiDAR to map the environment and place digital content within it weforum.org. As Cathy Hackl (Spatial Dynamics) explains, spatial computing is “the next evolution of computing” beyond screens – it extends digital interactions into the world around us weforum.org. In effect, we move from staring at flat monitors to engaging with floating images and data anchored to physical locations. Modern AR headsets and smart glasses, such as the Everysight Raptor, overlay contextual information on the real world (e.g., navigation, notifications, 3D models) weforum.org. Spatial computing leverages VR to create immersive digital worlds, and AR/MR to overlay information on our real surroundings weforum.org. For example, an AR navigation app could display arrows on the street in front of you, or a VR simulation could transport you to a virtual training site. The key is tracking: using sensors and computer vision, devices know where the user is looking or moving, enabling realistic interaction. Major tech companies are investing heavily in this space. Headsets like the Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro can switch between full VR and pass-through AR, blending modes at the user’s will xrtoday.com. Meanwhile, lightweight smart glasses (e.g. Everysight, referenced above) are emerging for on-the-go AR.
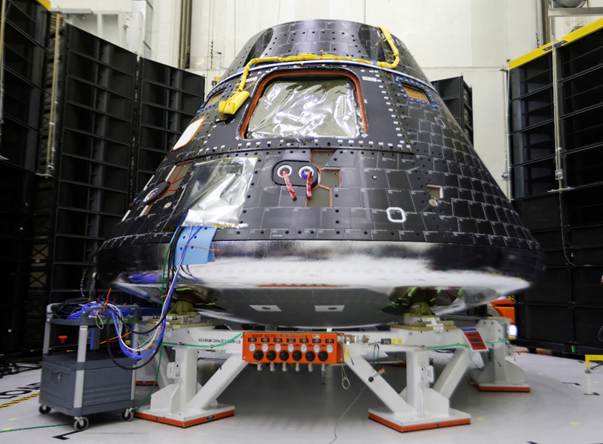

Figure 2: NASA’s Orion crew capsule (Artemis II mission). Engineers used HoloLens 2 AR headsets to guide the assembly of Orion’s crew module, overlaying holographic instructions onto the physical spacecraft weforum.org.
Real-World Applications of Spatial Computing
Spatial computing is already at work in many fields. In industry and engineering, AR-guided workflows boost efficiency and safety. For instance, Lockheed Martin used Microsoft HoloLens units (AR headsets) to assemble seats in NASA’s Orion spacecraft weforum.org. Technicians wore HoloLens 2 devices that overlaid holographic instructions directly onto the hardware – no printed manual was needed. Voice commands guided each step, and 3D models of the seats were superimposed on the real frame to show where bolts and panels should go weforum.org. This augmented approach cut labor hours dramatically. In fact, engineers reported 90% reductions in assembly time versus traditional methods weforum.org. In medical training, spatial computing offers lifelike simulations. Medical students can wear mixed-reality headsets to examine a 3D hologram of a beating heart, rotating it and interacting as if it were real tissueweforum.org. For example, Apple Vision Pro can display a fully functional heart model that behaves like a real heart – clinicians can reach out and probe it, gaining hands-on insight without cadaversweforum.org. Such immersive models help trainees learn anatomy and procedures in a safe, repeatable way. In entertainment and retail, immersive experiences are also on the rise. Marvel has hosted mixed-reality events where fans become part of superhero scenes weforum.org, and furniture retailers are using AR apps to let customers “place” virtual couches in their living rooms via smartphone. Even location-based AR games (e.g. Pokémon Go) are early examples of spatial computing in action. On the industrial side, companies are developing rugged VR/AR hardware for specialized uses – from AR maintenance glasses for factory workers to full-body VR rigs for firefighter training. The defence expo LAAD 2025, for example, showcased military personnel using VR headsets to simulate tactical scenarios, reflecting the trend toward customized XR hardware for enterprise xrtoday.com.

Figure 3: Conceptual illustration of an autonomous AI agent (center) assisting a human team. Modern immersive systems aim to empower people – here, an AI “assistant” is depicted helping engineers analyze data. As AWS notes, autonomous AI agents will move beyond chatbots to “reason, plan, and complete tasks in tandem with – or on behalf of – humans” aws.amazon.com.
AR/VR Hardware and Immersive Tech Trends
The hardware powering spatial computing is rapidly evolving. New headsets and wearables are getting lighter, more powerful and more comfortable xrtoday.comxrtoday.com. The latest devices often combine AR and VR seamlessly: the Meta Quest 3, for instance, can function as a standalone VR headset or “see-through” AR glasses without additional gear xrtoday.com. Apple’s Vision Pro likewise supports both fully immersive and mixed-reality modes. Importantly, these devices now include inside-out tracking (using built-in cameras and sensors) so no external base stations are needed. They also feature advanced hand and eye tracking, letting users interact by simply looking or gesturing, with no controllers xrtoday.com. This controller-free interaction makes the experience more natural and immersive.
Beyond headsets, a wider ecosystem of accessories is emerging. Haptic gloves and full-body suits are in development to provide tactile feedback – for example, simulating the feeling of touching virtual objects or the recoil of equipment. Advanced omnidirectional treadmills and motion platforms are also being tested to allow natural walking or driving in VR. Connectivity is another key trend: immersive applications demand high bandwidth and ultra-low latency. While 5G is helping, experts predict that even faster links (6G and beyond) will be needed to stream rich 3D content to wireless AR/VR glasses weforum.org.

Figure 4: How Spatial Computing in Enterprise Will Revolutionize Digital Transformation? (https://appinventiv.com/blog/spatial-computing-in-enterprise/)
AI Evolution: From Tools to Autonomous Agents
Parallel to the hardware revolution, AI has transformed dramatically over the past decades. Early AI systems were simple: rule-based programs and expert systems could perform limited tasks with heavy human guidance. Machine learning and then deep learning led to vast improvements. Milestones like IBM Watson (which won Jeopardy! in 2011) and OpenAI’s GPT-3 (2020) showed that AI could handle complex language and decision tasks wwt.com. GPT-3, for instance, endowed machines with surprisingly human-like conversational abilities wwt.com.
Today we are in the era of agentic (autonomous) AI. AI agents now can act on goals with minimal oversight. A useful definition: “An AI agent is a software system that perceives its environment, processes information, makes decisions and takes action to achieve a goal.” Such agents can be as simple as an email auto-responder or as complex as a robot navigating a warehouse wwt.com. Crucially, unlike traditional tools, modern AI agents plan and adapt. They learn from experience, adjust strategies, and can often generate new actions on their own.
To conceptualize this progress, AWS outlines levels of agent autonomy. In Level 1, an AI follows a fixed script (e.g. robotic process automation). By Level 3, an agent might be “given a goal” and autonomously plan, execute and adjust a multi-step workflow (for example, resolving a customer service ticket across multiple systems) aws.amazon.com. At Level 4, agents are fully autonomous: they set their own sub-goals, select or even create new tools, and learn from outcomes. These advanced agents can handle cross-domain tasks like strategic research or complex project management aws.amazon.com.
The shift to autonomous AI is already underway. In fact, AWS and others note that AI agents are no longer mere scripts: they can “reason iteratively, evaluate outcomes, adapt plans, and pursue goals without ongoing human input” aws.amazon.com. Gartner predicts that by 2028, 15% of work decisions will be made by such agentic AI (up from virtually 0% today) aws.amazon.com. The market is growing accordingly. For example, biotech firms like Genentech are building AI agent systems to automate literature search and data analysis, freeing scientists to focus on high-level research aws.amazon.com. Large enterprises (Amazon, banks, manufacturing) are piloting “digital assistants” that autonomously optimize workflows, migrate software versions, or give personalized financial advice, often with significant cost savings aws.amazon.comaws.amazon.com.
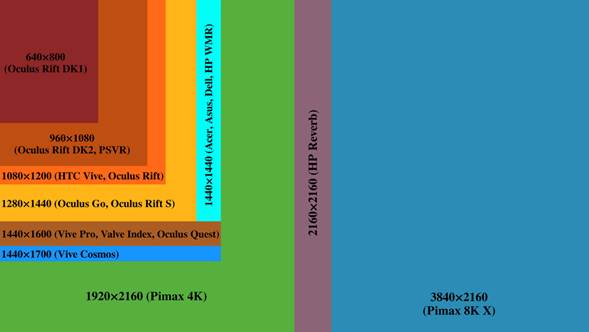
Figure 5: Comparison of VR headset display resolutions per eye (higher = sharper image). Chart: Veikko Mäkelä, CC BY-SA. Modern VR/AR headsets vary in resolution and field-of-view, affecting image clarity commons.wikimedia.org. Continuous hardware improvements (more pixels per eye, wider FOV) are driving more realistic immersive experiences.
Autonomous AI & Spatial Computing: The Future
Looking ahead, spatial computing and autonomous AI are poised to converge. Imagine AI-driven virtual assistants that live in our augmented reality environment: they could appear as holographic avatars, recognize objects around us, and carry out complex tasks. For instance, an AI agent could walk you through repairing a machine by highlighting parts and speaking instructions, combining AR visualization with on-the-fly natural language reasoning. In factories, fleets of AI-augmented robots might navigate spaces guided by spatial maps, communicating with each other and with human workers in real time.
Key enabling technologies are already aligning. Large language models and 3D vision models (the same advances powering ChatGPT and modern AR) are making spatial computers smarter at understanding context weforum.org. Game engines and simulation environments are being used both to train AI and to deliver smooth interactive worlds for AR/VR. On the infrastructure side, next-gen wireless networks will allow ubiquitous headset use indoors and out. Researchers are also working on brain-computer interfaces and AI sensors, hinting at even deeper integration between mind, machine and space.
As these technologies mature, we must also consider challenges. New forms of privacy and security will emerge: for example, spatial computing raises questions about “virtual air rights” – who can project content into shared physical spaces? Likewise, autonomous agents need clear governance. Many experts advocate developing AI ethics frameworks and standards as these systems become more like collaborators than tools aws.amazon.com. In summary, spatial computing and autonomous AI agents are reshaping the tech landscape in tandem. The fusion of AR/VR with AI is enabling fully immersive, interactive applications—from enhanced collaboration to life-like simulations weforum.orgweforum.org. Meanwhile, AI’s evolution means those applications will increasingly act intelligently on our behalf. For tech-savvy readers, the implication is clear: the next wave of innovation will make digital experiences more physical than ever, with smart agents and environments working together to augment human capability.